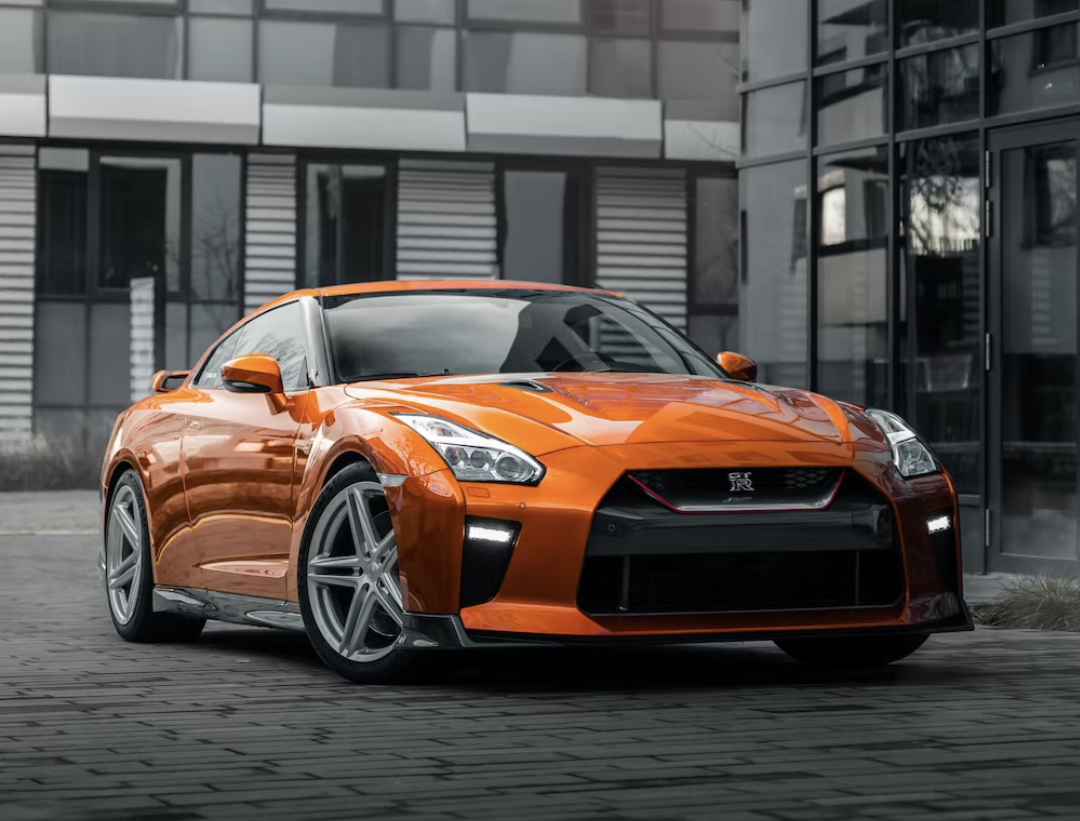
Engine Details
The first cars named "Skyline GT-R" were produced between 1969 and 1972 under the model code KPGC10, and were successful in Japanese touring car racing events. This model was followed by a brief production run of second-generation cars, under model code KPGC110, in 1973. (1) (1)Wikipedia
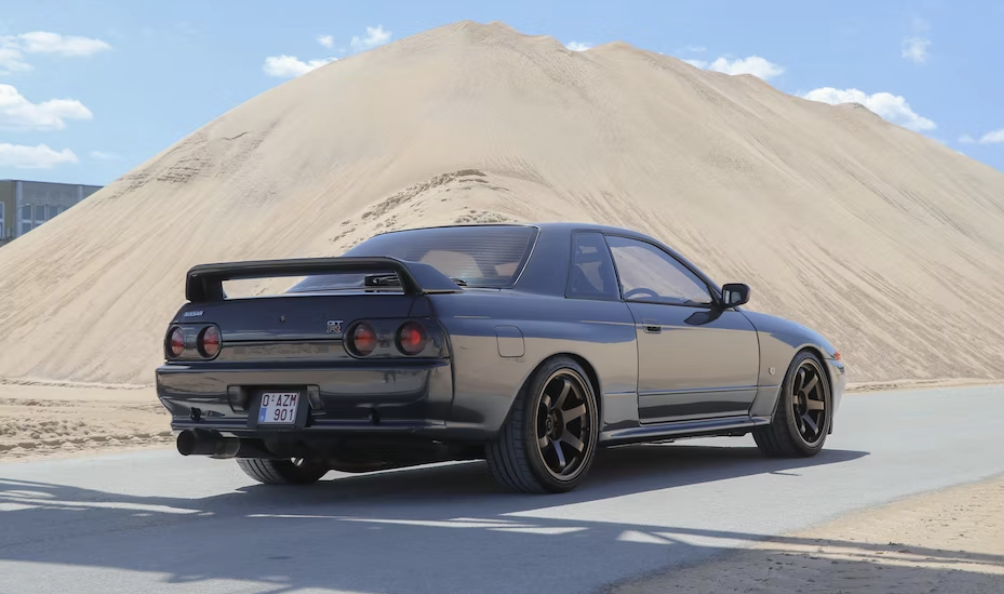
Chasis and Suspension
By the time the Skyline H/T 2000GT-R was produced, now in a coupe body style, the GT-R racked up its 50th overall racing victory. The following year, the KPGC110 hit the market, but after a production run of a mere 197 units, Nissan pulled the plug on the GT-R, citing stricter emissions standards and the international oil crisis as the main reasons. The GT-R would not be seen for another 16 years. (2)
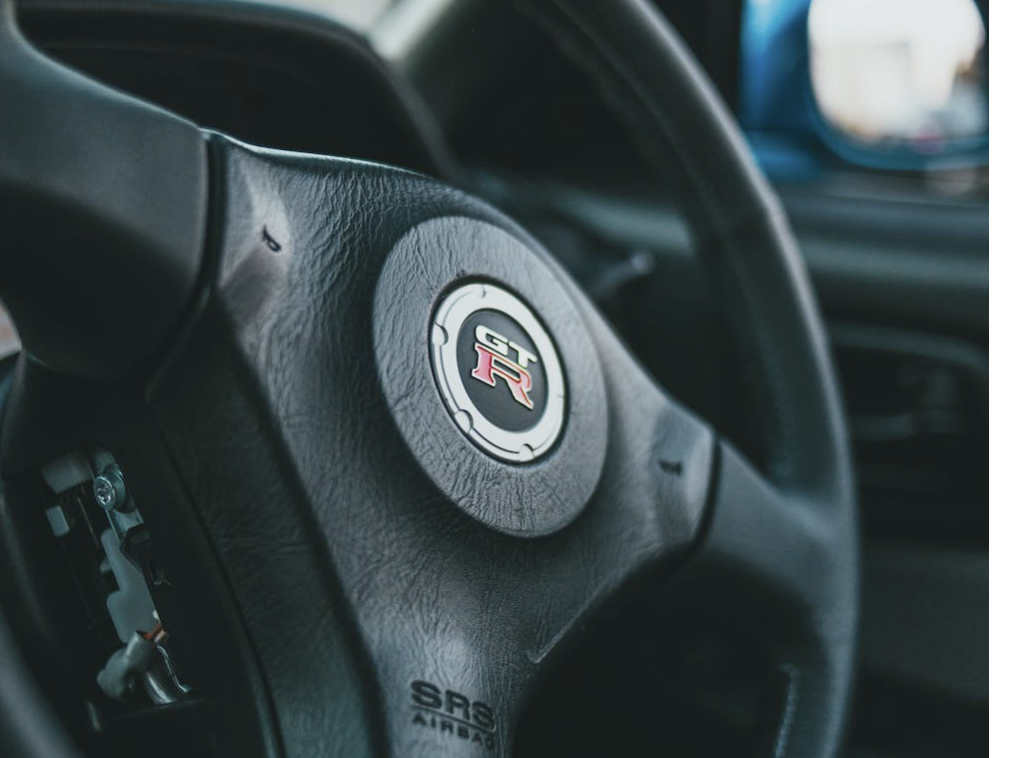
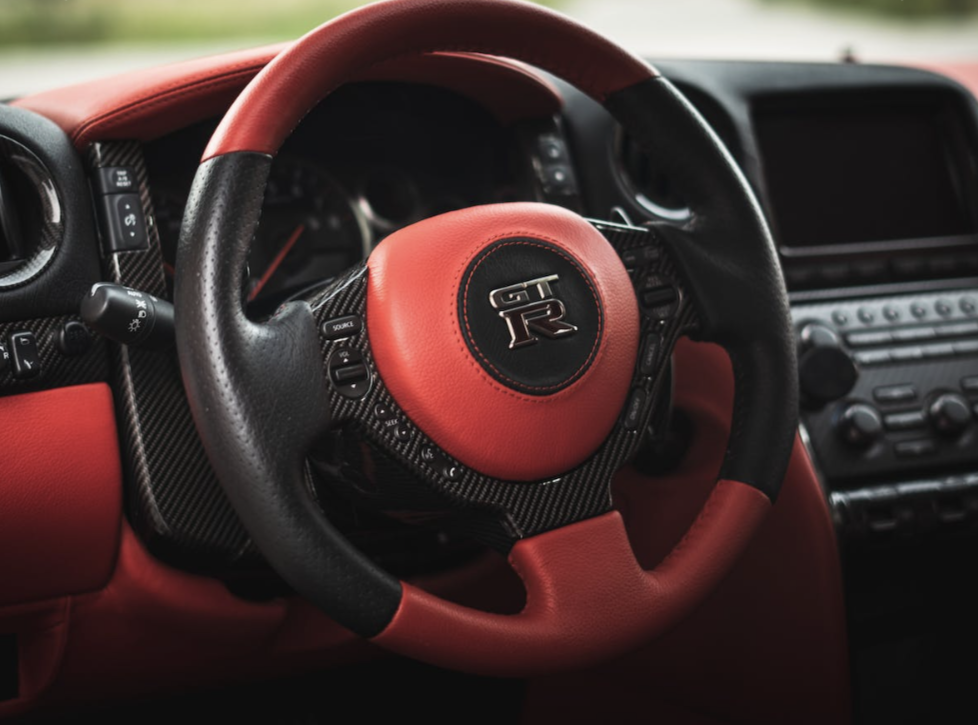
Interior
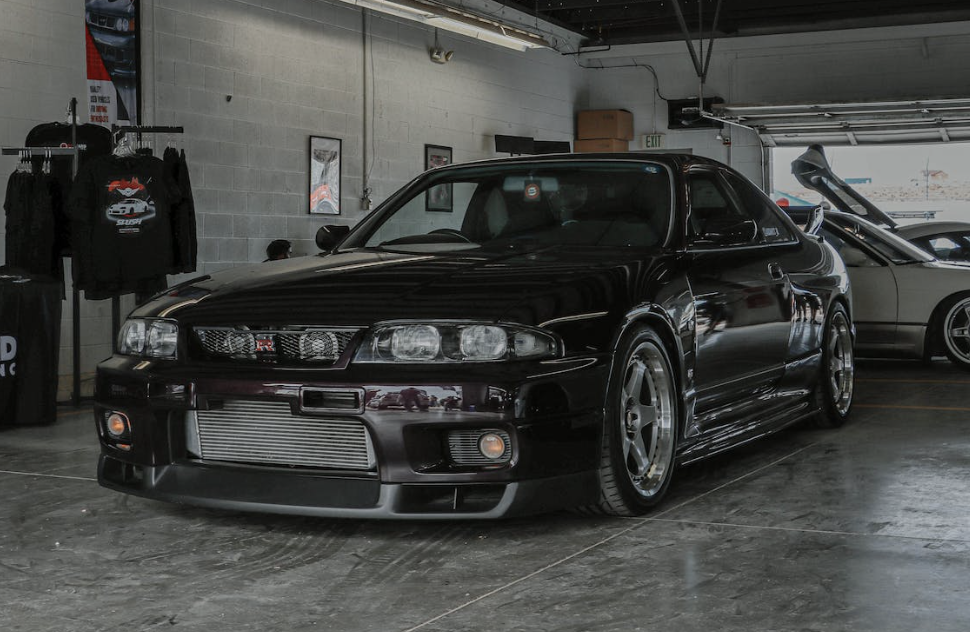
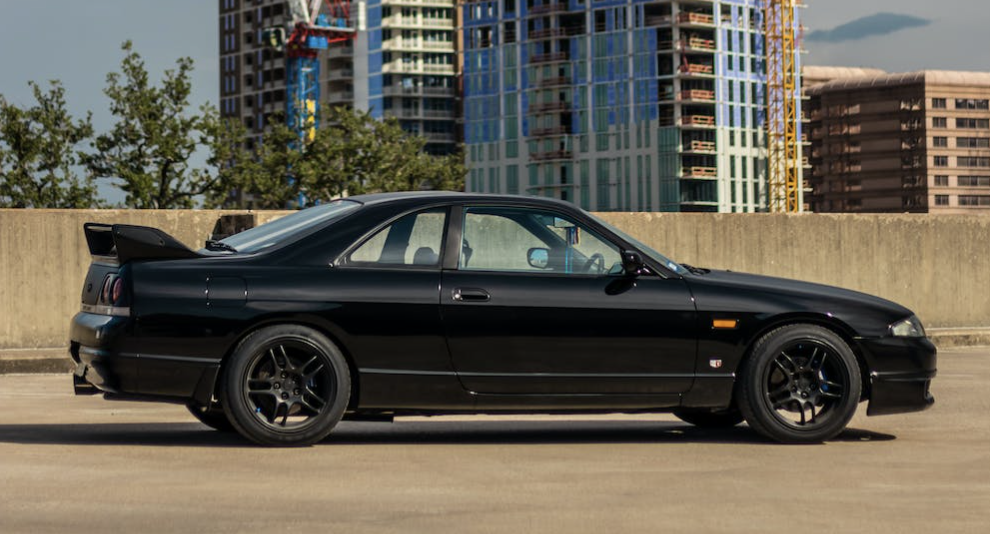
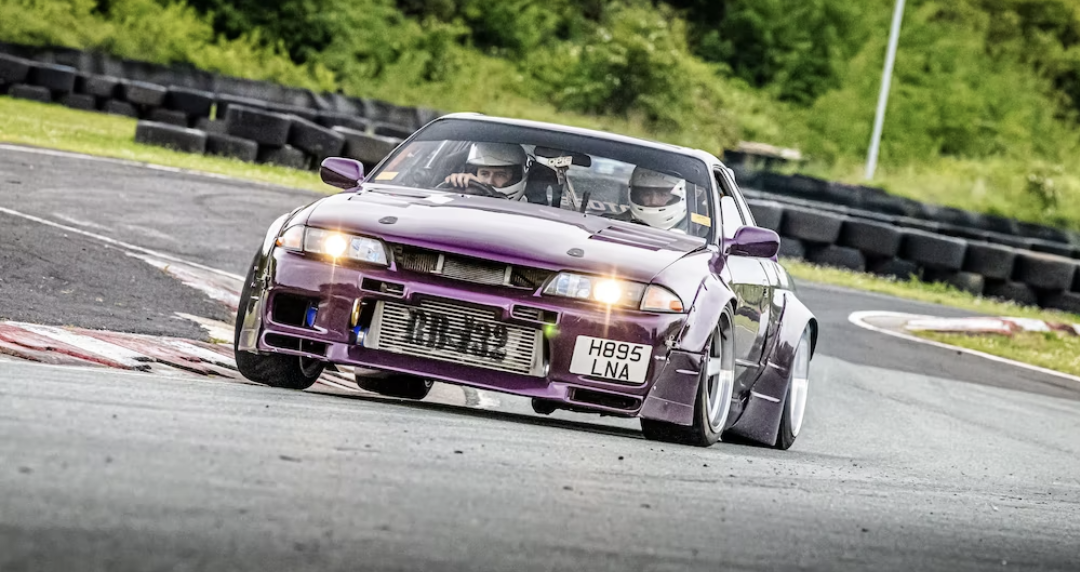
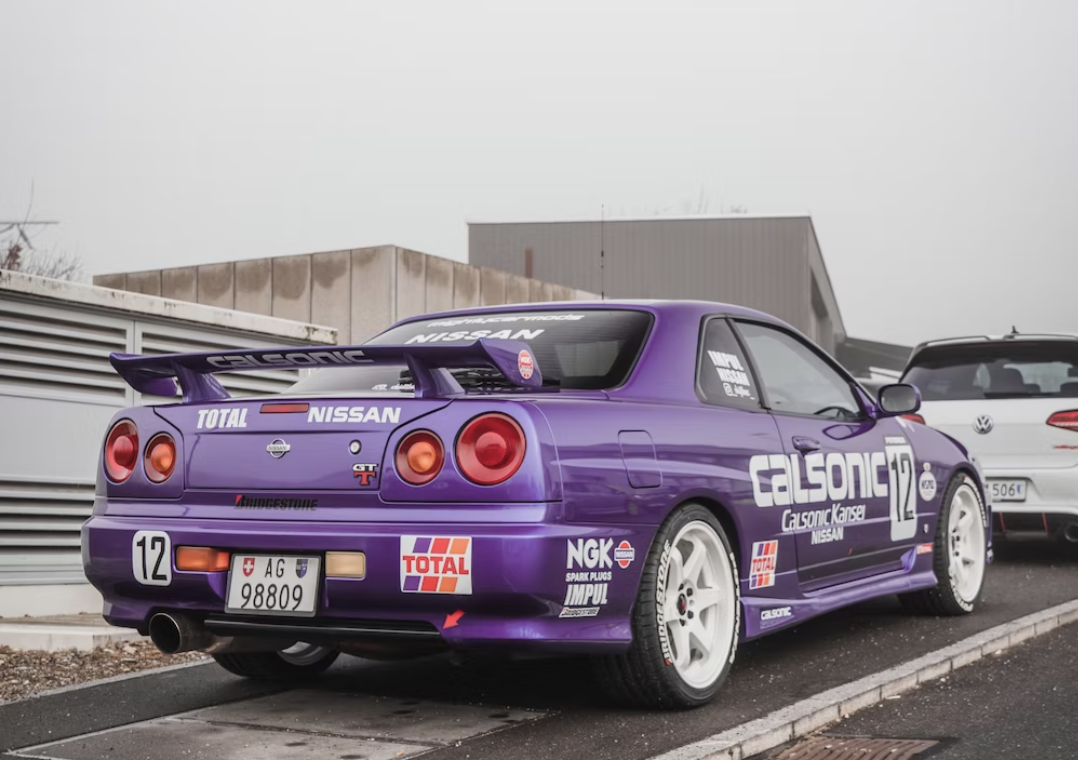
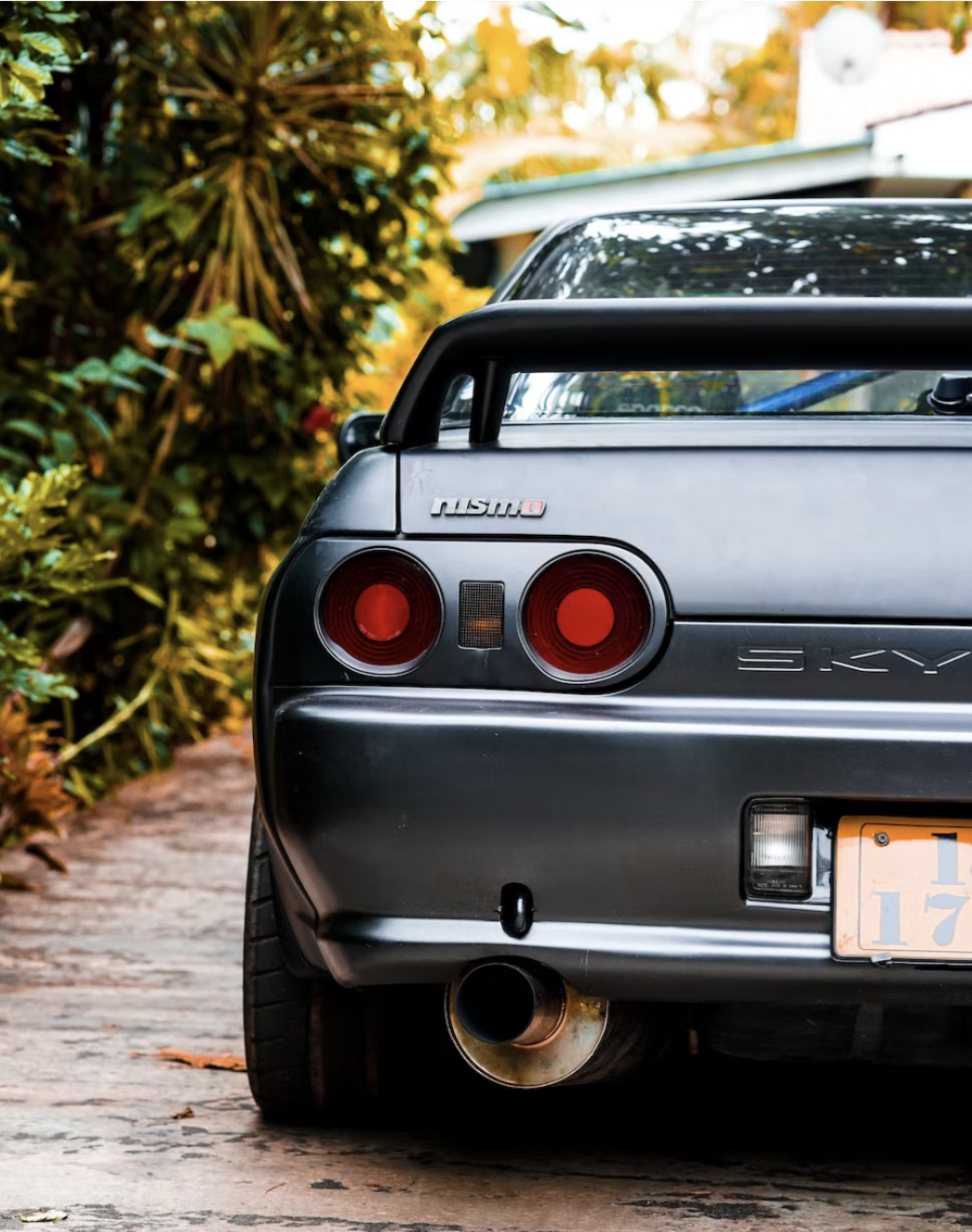
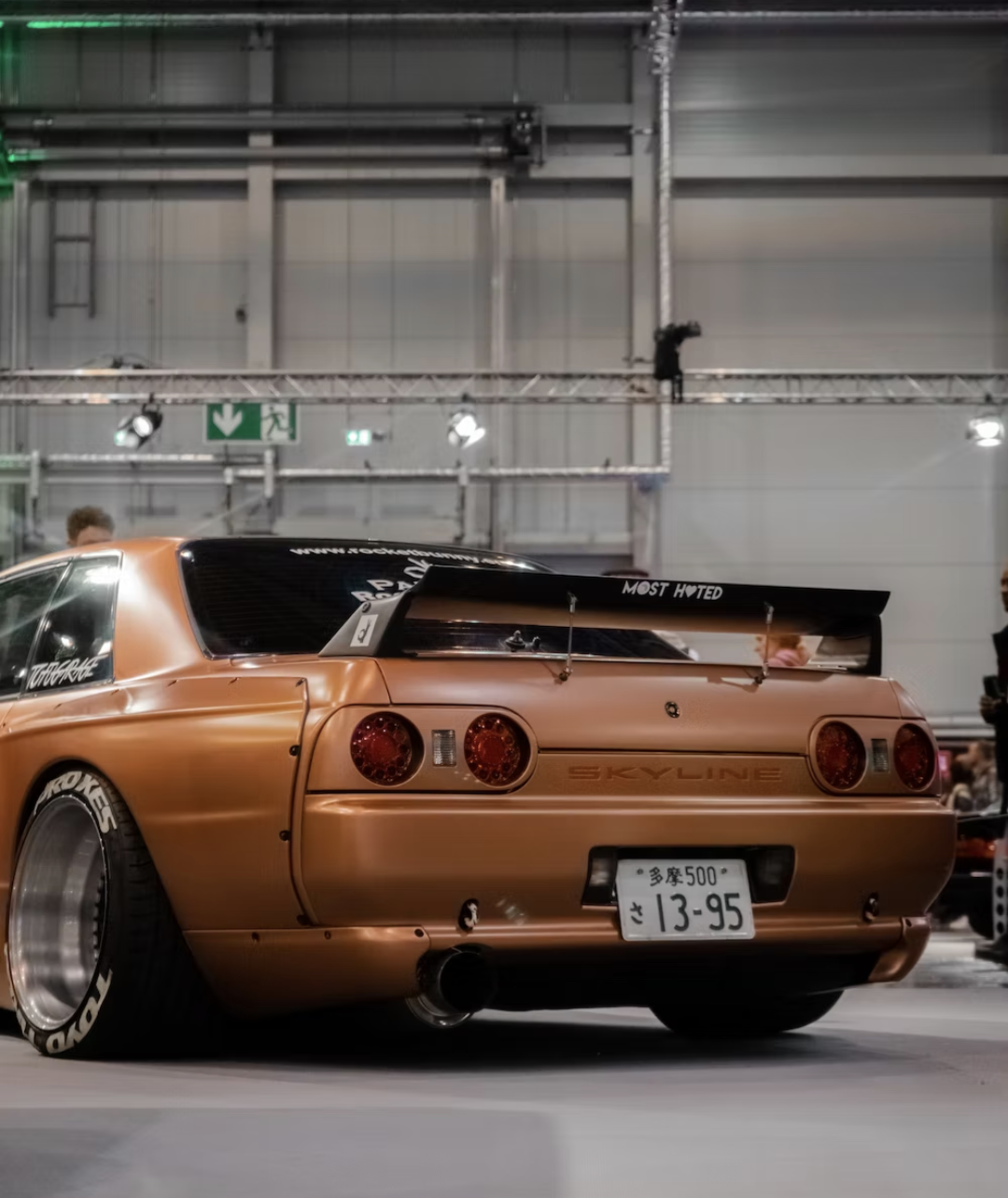
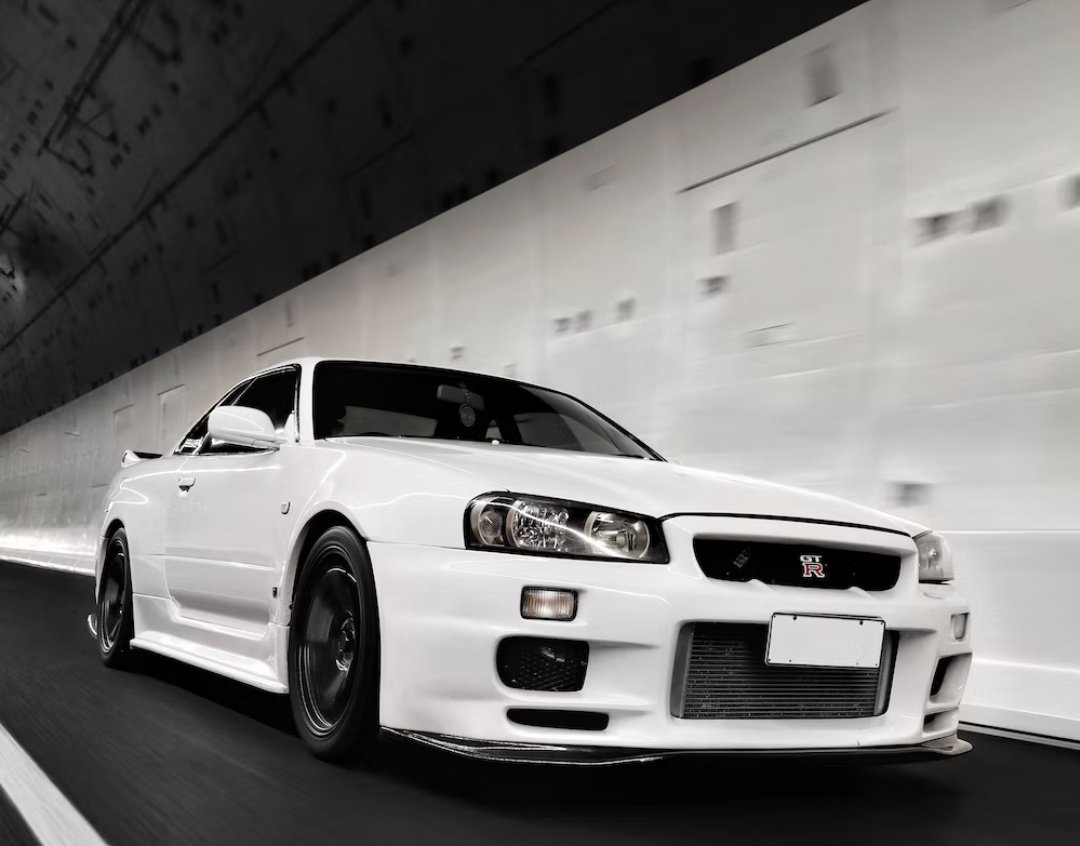
The modern-day GT-R took the Japanese automotive market by storm when it was launched in August 1989. It featured all-wheel Super HICAS steering, awd and a turbocharged inline-6, the RB26DETT, which pumped out 280 bhp and 260 lb.-ft. of torque. Legend has it that chief engineer Shurei Ito didn't reveal to anyone, including his own team members, that this car would wear the GT-R banner until right before its debut. (2)
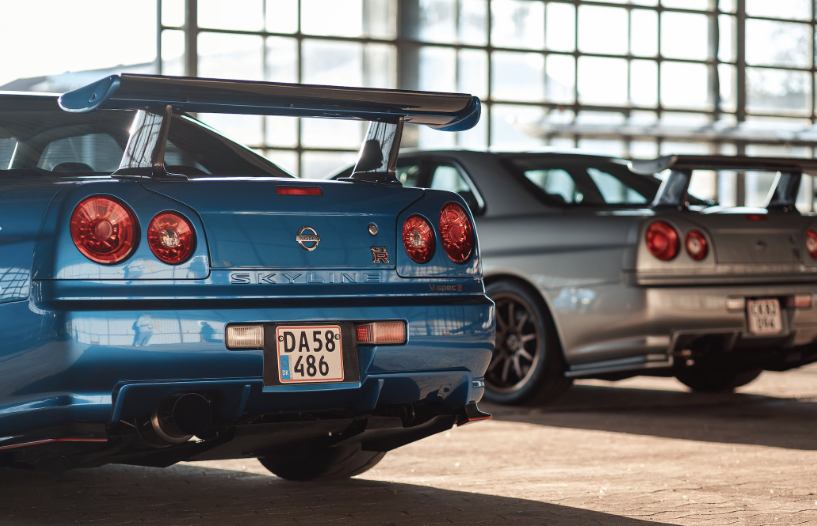
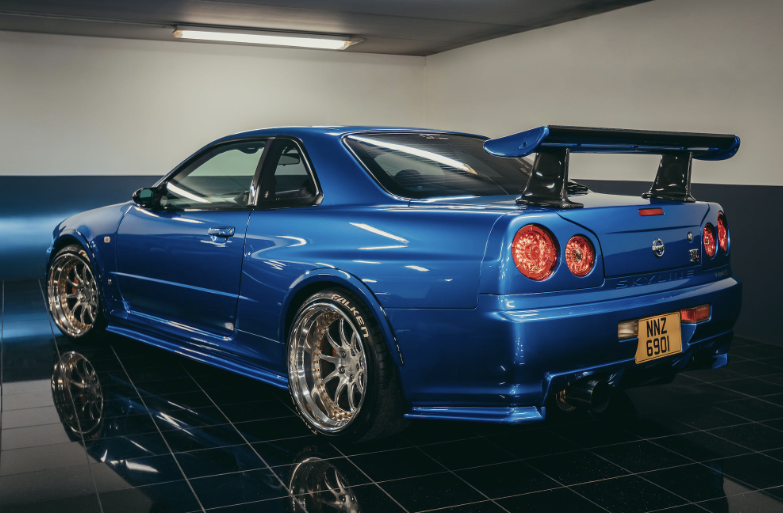
Exterior
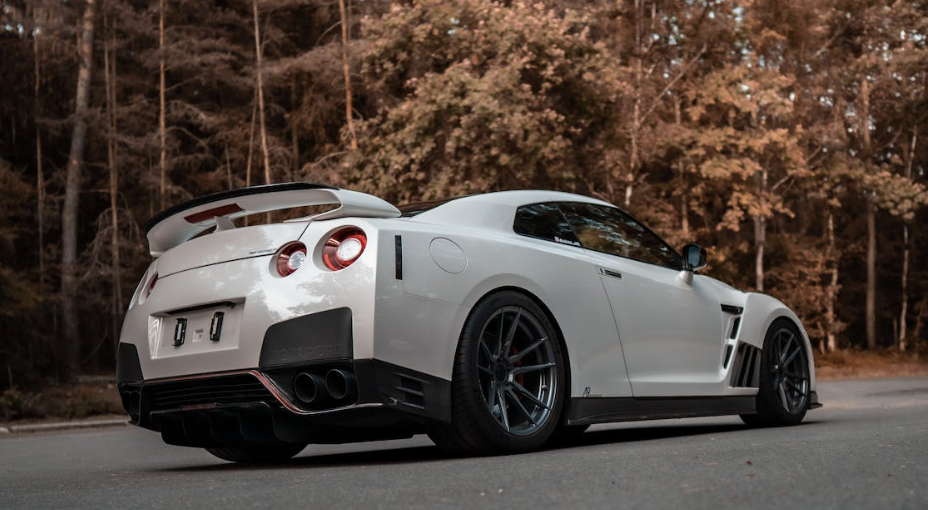
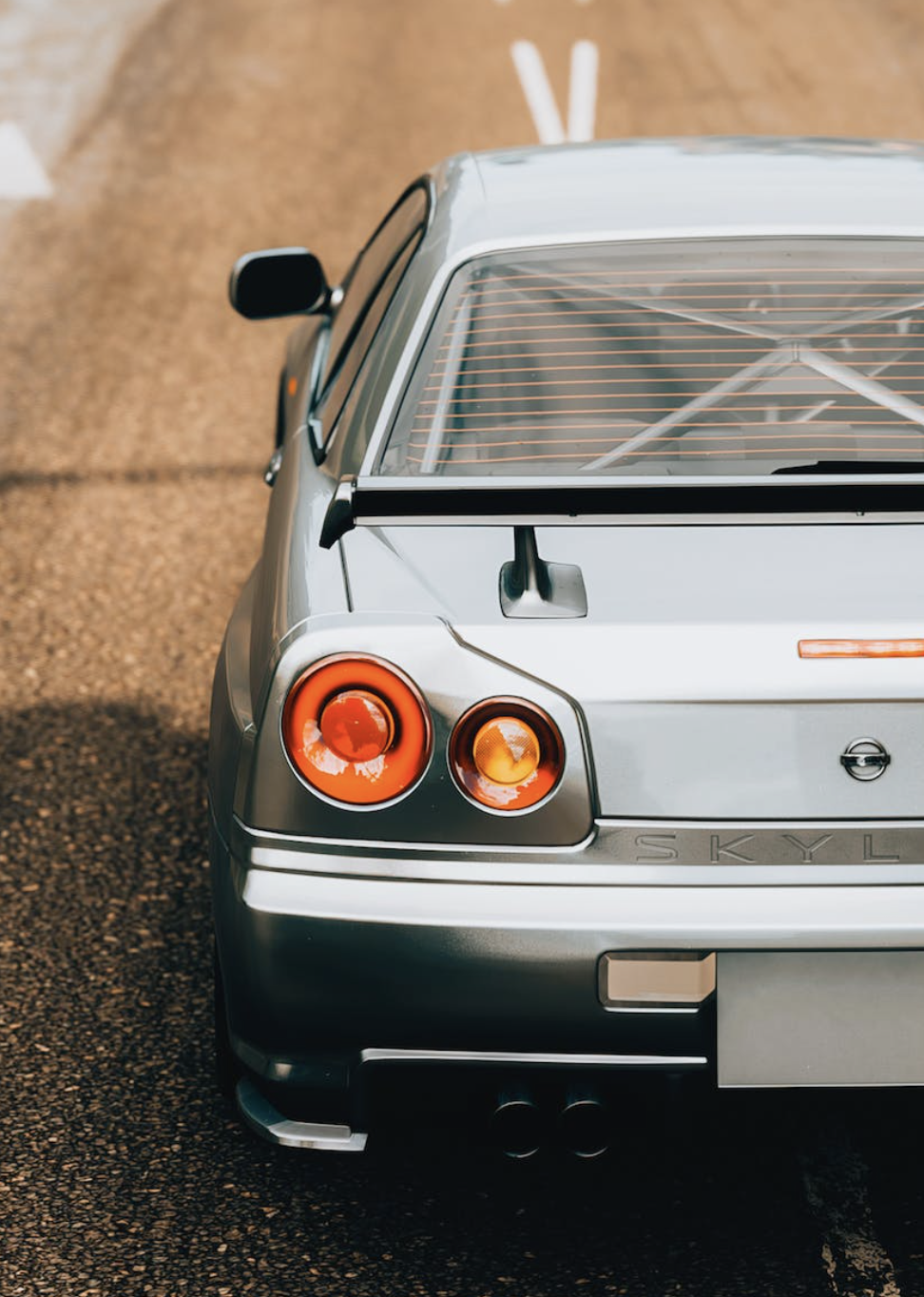
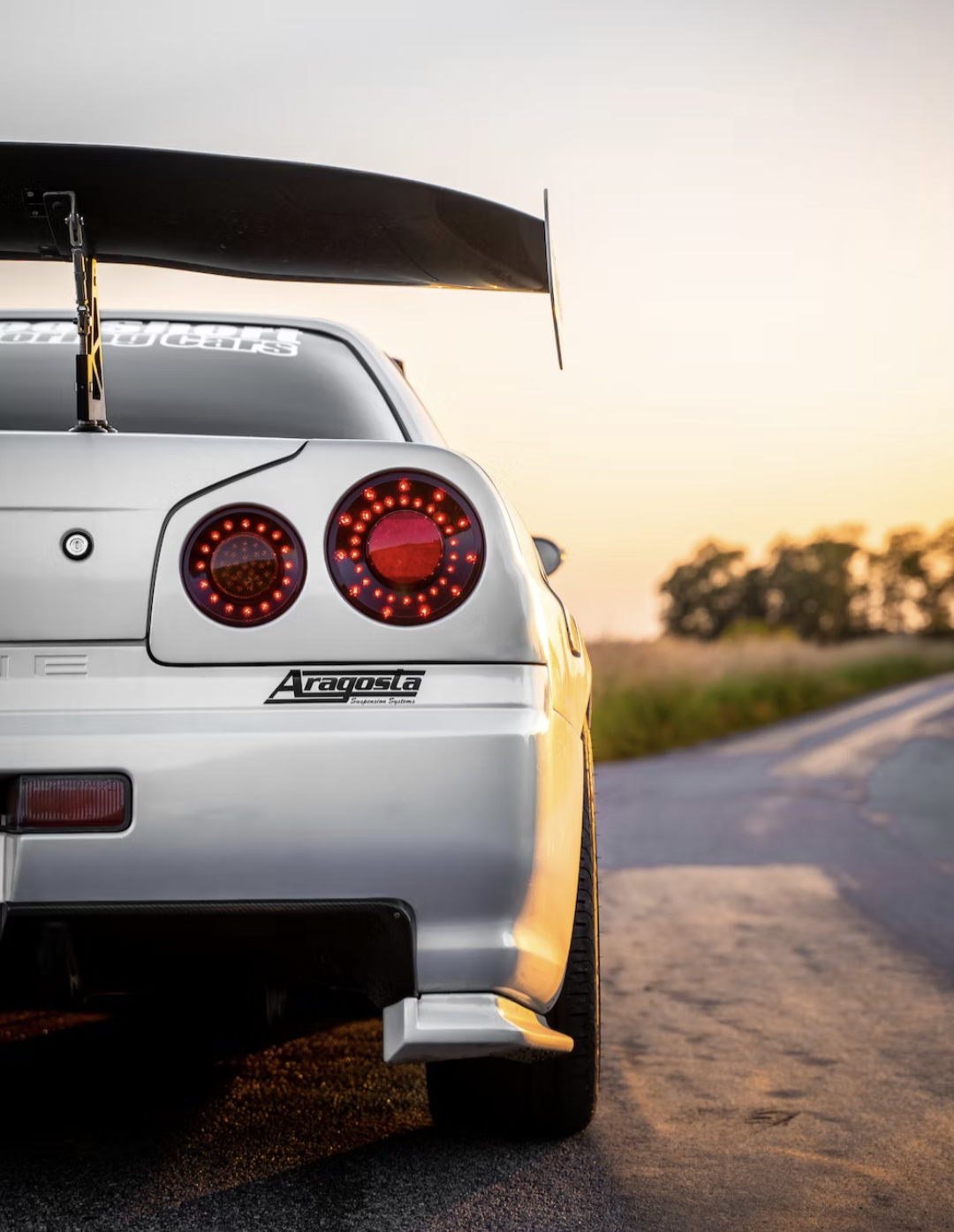
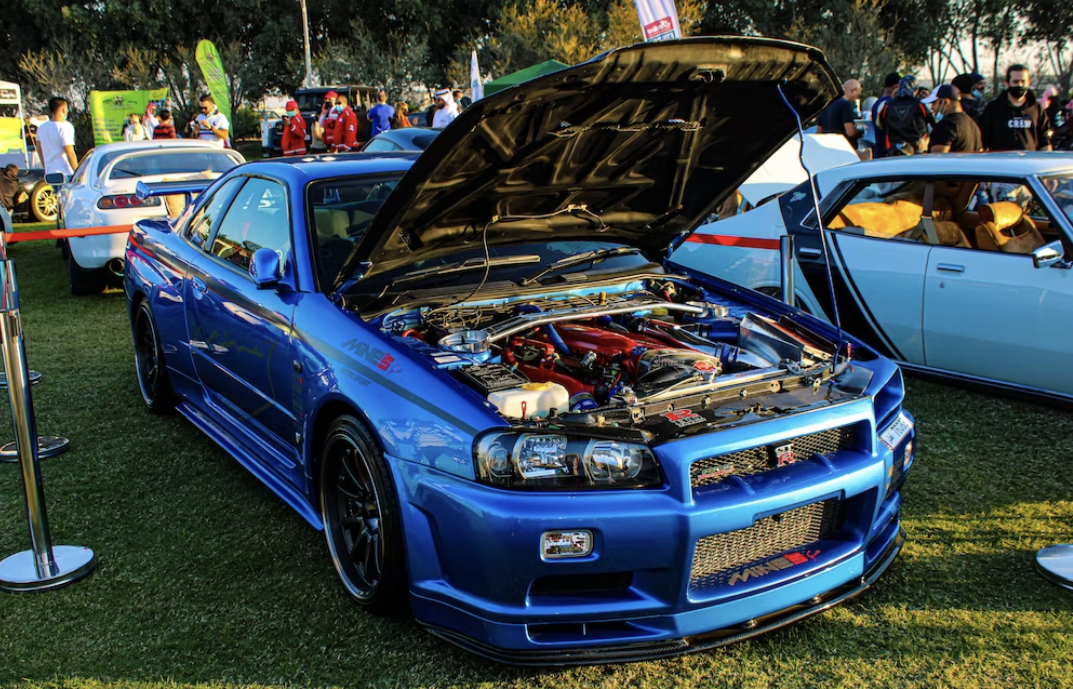
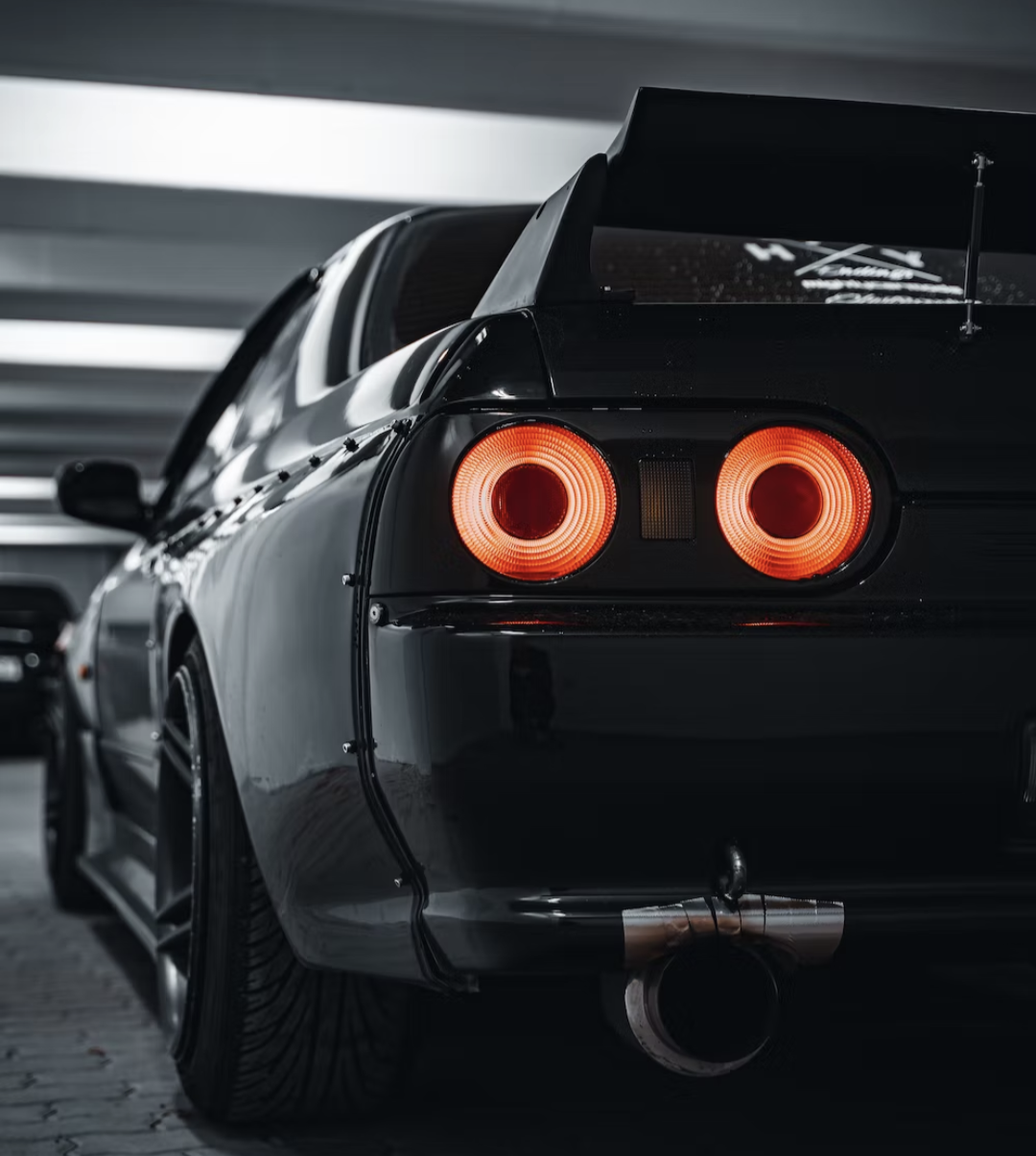
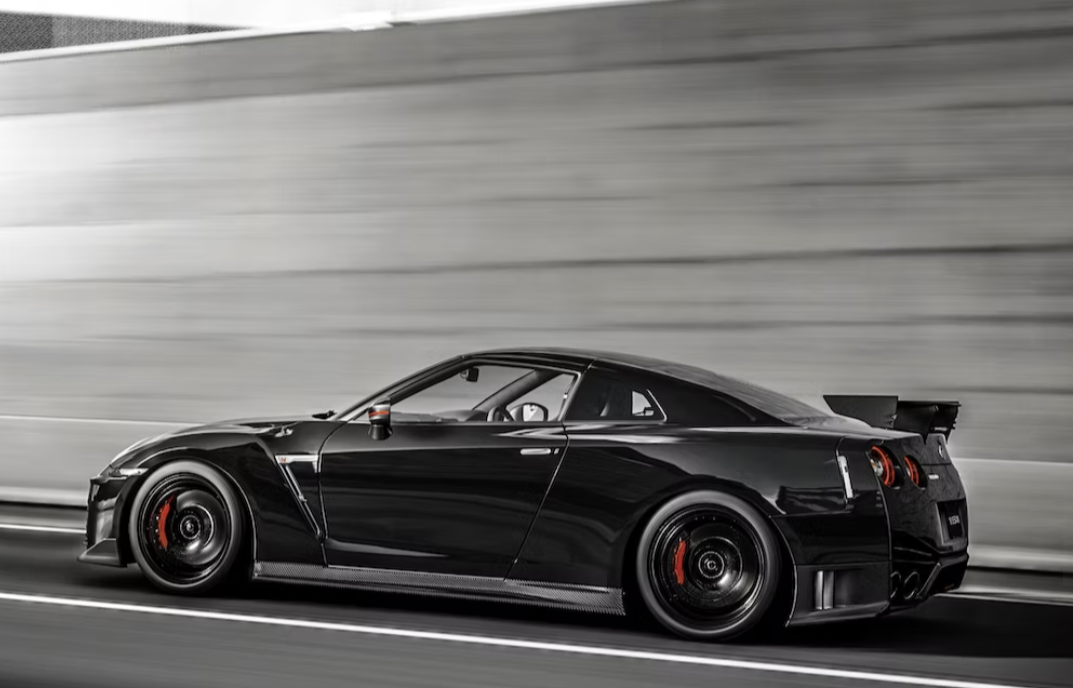
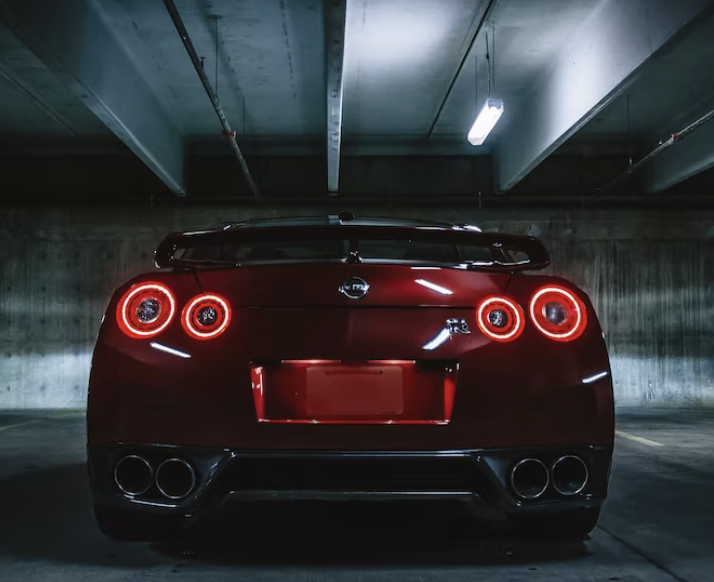
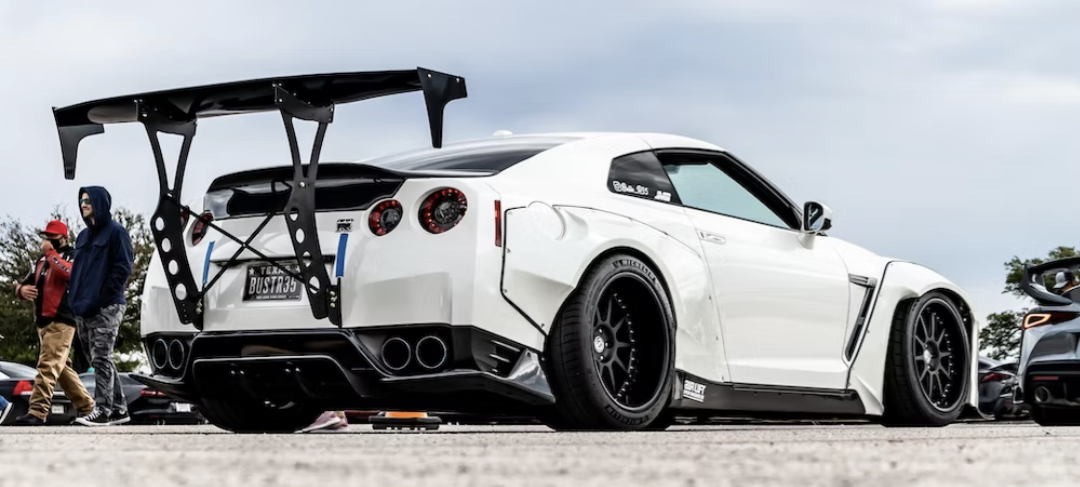
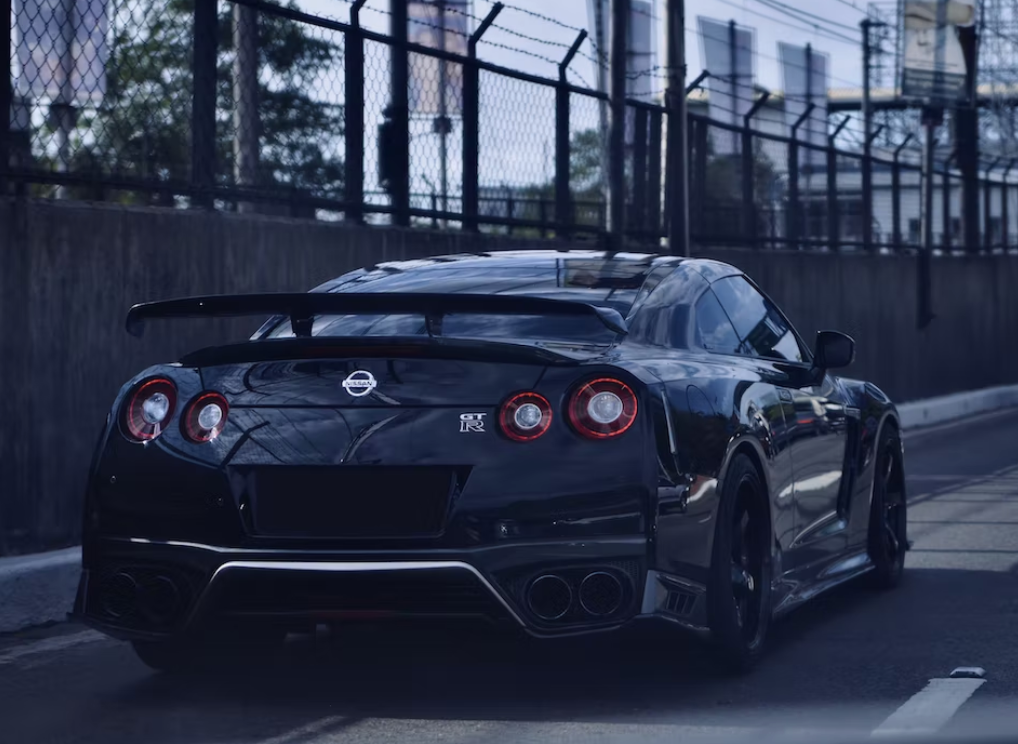
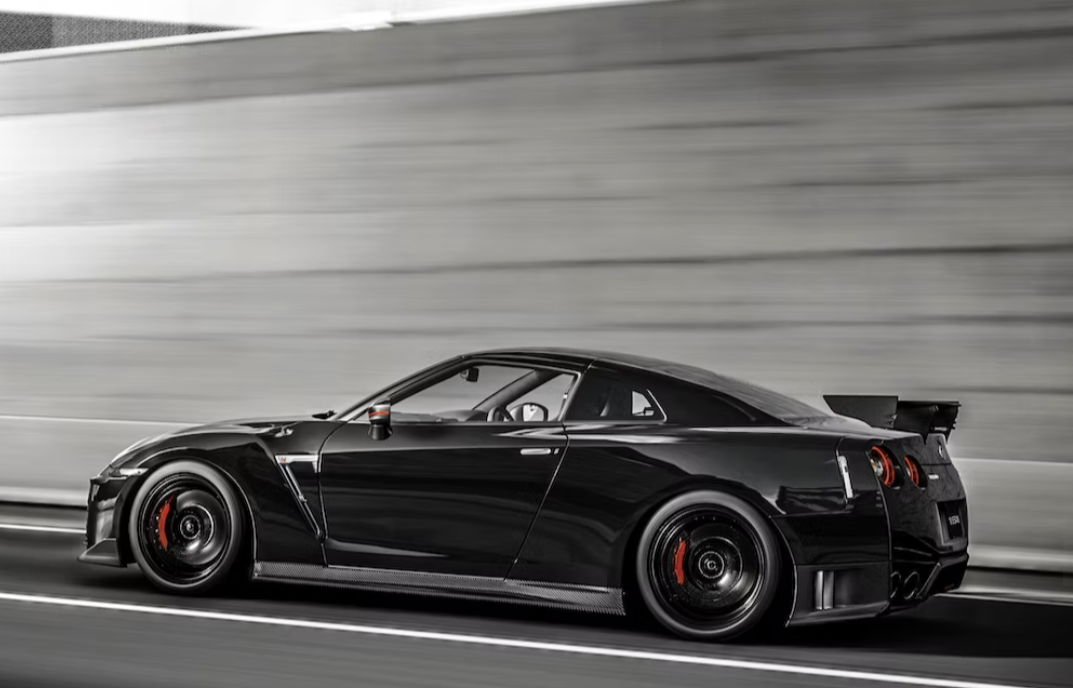
The most technologically advanced GT-R yet, the R34 would be the last GT-R to be powered by the RB26DETT. While horsepower was officially rated at 280 bhp, aftermarket tuners like HKS and Mine's were cranking out versions with up to 800 bhp. Also, the R34 made a formidable race car, with the Pennzoil Nismo GT-R winning the Japanese Grand Touring Championship in 1999. The R34 was featured numerous times in R&T. Production stopped in 2002. (2) (2)https://www.roadandtrack.com/car-culture/a13650/the-history-of-the-nissan-gt-r/ Xxxxxx